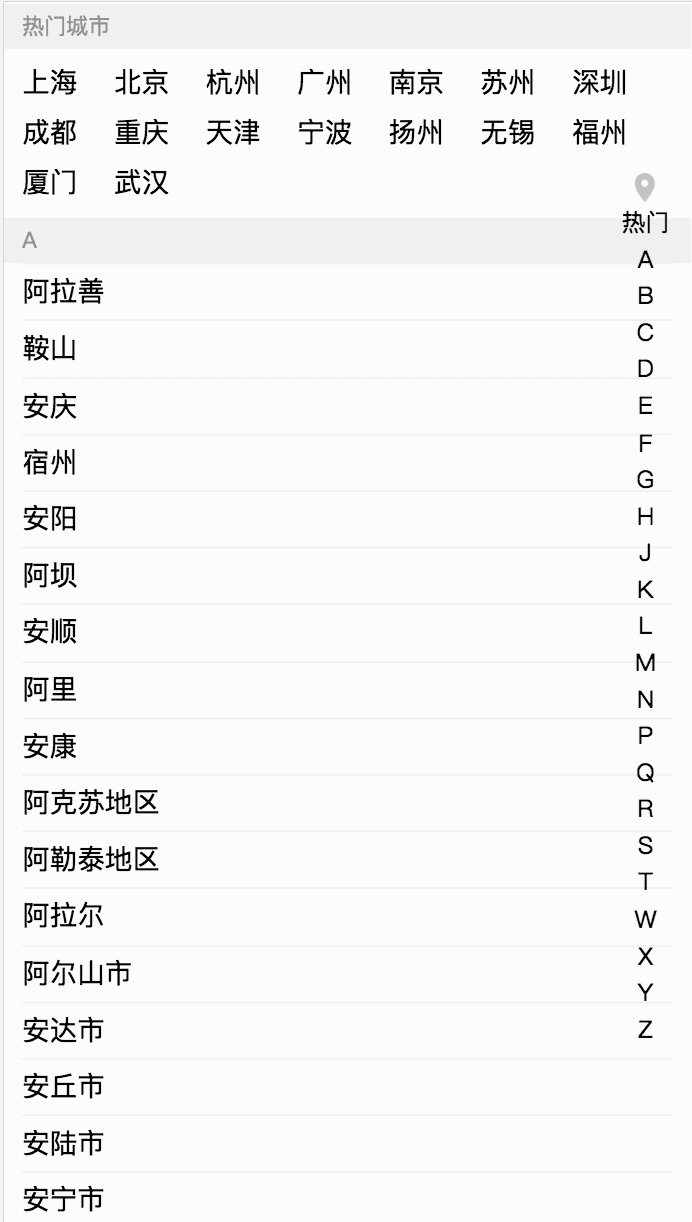
Recently, I’ve been using the React technology stack to refactor a single-page application. One of the pages implements a city selection function, mainly to quickly jump to the corresponding position based on the first letter of the city, similar to the phone contact search function in native apps. The page is shown in the figure:

Main Problem#
When sliding up and down the right-side fixed positioned element, the page will scroll along with it.

Of course, this phenomenon should be frequently encountered during development. For example, when a modal box pops up, if the modal box content height is less than the box height, sliding the content will also cause the page to scroll along. So in React, handle it as usual:
<div className="nonius"
id="nonius"
onTouchStart={this.sidebarTouchStart.bind(this)}
onTouchMove={this.sidebarTouchMove.bind(this)}
onTouchEnd={this.sidebarTouchEnd.bind(this)}
>
Using React’s event binding mechanism, bind three handlers respectively. In the onTouchMove event, I hope to prevent the parent element’s scrolling through preventDefault:
sidebarTouchMove(e) {
e.preventDefault();
}
Problem Analysis#
The issue occurs because:
- Touch event propagation - Touch events bubble up to parent elements
- Default behavior - Browser’s default scroll behavior isn’t prevented
- Event handling - React’s synthetic events don’t always prevent native behavior
- CSS overflow - Parent elements may have scrollable content
Solutions#
1. Basic Event Prevention#
// Prevent default touch behavior
sidebarTouchMove(e) {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
}
// For React synthetic events
sidebarTouchMove(e) {
e.nativeEvent.preventDefault();
e.nativeEvent.stopPropagation();
}
2. CSS-Based Solution#
/* Prevent scrolling on the body */
body {
overflow: hidden;
}
/* Or target specific container */
.scroll-container {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100vh;
}
/* For fixed positioned elements */
.fixed-element {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
right: 0;
height: 100vh;
overflow-y: auto;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
3. JavaScript Solution with Body Lock#
class ScrollPrevention {
constructor() {
this.scrollY = 0;
this.isLocked = false;
}
lock() {
if (this.isLocked) return;
this.scrollY = window.scrollY;
document.body.style.position = 'fixed';
document.body.style.top = `-${this.scrollY}px`;
document.body.style.width = '100%';
this.isLocked = true;
}
unlock() {
if (!this.isLocked) return;
document.body.style.position = '';
document.body.style.top = '';
document.body.style.width = '';
window.scrollTo(0, this.scrollY);
this.isLocked = false;
}
}
// Usage in React component
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.scrollPrevention = new ScrollPrevention();
}
componentDidMount() {
this.scrollPrevention.lock();
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.scrollPrevention.unlock();
}
}
4. React Hook Solution#
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
const useScrollLock = (isLocked) => {
const scrollY = useRef(0);
useEffect(() => {
if (isLocked) {
// Lock scroll
scrollY.current = window.scrollY;
document.body.style.position = 'fixed';
document.body.style.top = `-${scrollY.current}px`;
document.body.style.width = '100%';
} else {
// Unlock scroll
document.body.style.position = '';
document.body.style.top = '';
document.body.style.width = '';
window.scrollTo(0, scrollY.current);
}
return () => {
// Cleanup on unmount
document.body.style.position = '';
document.body.style.top = '';
document.body.style.width = '';
};
}, [isLocked]);
};
// Usage
function MyComponent() {
const [isModalOpen, setIsModalOpen] = useState(false);
useScrollLock(isModalOpen);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setIsModalOpen(true)}>Open Modal</button>
{isModalOpen && (
<Modal onClose={() => setIsModalOpen(false)} />
)}
</div>
);
}
5. Touch Event Handling#
class TouchScrollHandler {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.startY = 0;
this.startX = 0;
this.isScrolling = false;
this.bindEvents();
}
bindEvents() {
this.element.addEventListener('touchstart', this.handleTouchStart.bind(this), { passive: false });
this.element.addEventListener('touchmove', this.handleTouchMove.bind(this), { passive: false });
this.element.addEventListener('touchend', this.handleTouchEnd.bind(this), { passive: false });
}
handleTouchStart(e) {
this.startY = e.touches[0].clientY;
this.startX = e.touches[0].clientX;
this.isScrolling = false;
}
handleTouchMove(e) {
const currentY = e.touches[0].clientY;
const currentX = e.touches[0].clientX;
const diffY = Math.abs(currentY - this.startY);
const diffX = Math.abs(currentX - this.startX);
// Determine if this is a vertical scroll
if (diffY > diffX) {
this.isScrolling = true;
e.preventDefault();
}
}
handleTouchEnd(e) {
this.isScrolling = false;
}
destroy() {
this.element.removeEventListener('touchstart', this.handleTouchStart);
this.element.removeEventListener('touchmove', this.handleTouchMove);
this.element.removeEventListener('touchend', this.handleTouchEnd);
}
}
6. React Component Implementation#
import React, { useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
const ScrollableElement = ({ children, className, ...props }) => {
const elementRef = useRef(null);
const touchHandlerRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (elementRef.current) {
touchHandlerRef.current = new TouchScrollHandler(elementRef.current);
}
return () => {
if (touchHandlerRef.current) {
touchHandlerRef.current.destroy();
}
};
}, []);
return (
<div
ref={elementRef}
className={className}
{...props}
>
{children}
</div>
);
};
// Usage
function CitySelector() {
return (
<div className="city-selector">
<div className="city-list">
{/* City list content */}
</div>
<ScrollableElement className="alphabet-navigator">
{/* Alphabet navigation */}
</ScrollableElement>
</div>
);
}
Advanced Solutions#
1. Intersection Observer Approach#
const useScrollPrevention = (elementRef, isActive) => {
useEffect(() => {
if (!isActive || !elementRef.current) return;
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(
(entries) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
// Element is visible, prevent scroll
document.body.style.overflow = 'hidden';
} else {
// Element is not visible, allow scroll
document.body.style.overflow = '';
}
});
},
{ threshold: 0.1 }
);
observer.observe(elementRef.current);
return () => {
observer.disconnect();
document.body.style.overflow = '';
};
}, [isActive, elementRef]);
};
2. CSS Containment#
.scroll-container {
contain: layout style paint;
overflow: hidden;
}
.scrollable-content {
contain: layout style paint;
overflow-y: auto;
height: 100%;
}
3. Passive Event Listeners#
// Use passive: false to allow preventDefault
element.addEventListener('touchmove', handler, { passive: false });
// In React
<div
onTouchMove={(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
}}
style={{ touchAction: 'none' }}
>
Content
</div>
Common Pitfalls#
1. Event Propagation Issues#
// Bad: Event still propagates
handleTouchMove(e) {
e.preventDefault();
// Event still bubbles up
}
// Good: Stop propagation
handleTouchMove(e) {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
}
2. CSS Overflow Conflicts#
/* Bad: Conflicting overflow settings */
.container {
overflow: hidden;
}
.scrollable {
overflow: auto; /* This might not work as expected */
}
/* Good: Clear hierarchy */
.container {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100vh;
}
.scrollable {
overflow-y: auto;
height: 100%;
}
3. Memory Leaks#
// Bad: Not cleaning up event listeners
useEffect(() => {
const handler = new TouchScrollHandler(element);
// No cleanup
}, []);
// Good: Proper cleanup
useEffect(() => {
const handler = new TouchScrollHandler(element);
return () => {
handler.destroy();
};
}, []);
Best Practices#
1. Use CSS When Possible#
/* Prefer CSS solutions for simple cases */
.modal-open {
overflow: hidden;
}
2. Handle Edge Cases#
// Check if element is scrollable
const isScrollable = (element) => {
return element.scrollHeight > element.clientHeight;
};
// Only prevent scroll if element is scrollable
if (isScrollable(element)) {
element.addEventListener('touchmove', preventDefault, { passive: false });
}
3. Test on Different Devices#
// Test touch events on different devices
const isTouchDevice = () => {
return 'ontouchstart' in window || navigator.maxTouchPoints > 0;
};
if (isTouchDevice()) {
// Apply touch-specific solutions
}
Conclusion#
Preventing page scroll in React applications requires understanding:
- Event handling - How touch events propagate and can be prevented
- CSS properties - Using overflow and position to control scrolling
- JavaScript solutions - Programmatically managing scroll behavior
- React patterns - Using hooks and components for scroll management
Key Solutions:#
- Event prevention - Use
preventDefault()andstopPropagation() - CSS overflow - Control scrolling with CSS properties
- Body locking - Temporarily disable body scroll
- Touch handling - Custom touch event management
- React hooks - Reusable scroll prevention logic
Best Practices:#
- Use CSS first - Simple cases can be solved with CSS
- Handle cleanup - Always clean up event listeners and styles
- Test thoroughly - Test on different devices and browsers
- Consider accessibility - Ensure solutions don’t break accessibility
- Performance - Use efficient event handling and CSS
By understanding these concepts and applying the appropriate solutions, you can effectively prevent unwanted page scrolling in React applications while maintaining good user experience and performance.